Difference Between Hot Chamber and Cold Chamber Die Casting
Published: 23 Jul 2025
Understanding the difference between hot chamber and cold chamber die casting is key if you’re working with metal manufacturing. Both techniques are used to form precise metal parts, but they operate differently and rely on distinct materials. Whether you’re choosing a process for speed, metal type, or cost, knowing how they differ will help you make the right decision. Let’s break down what sets these two casting types apart.
Hot Chamber vs Cold Chamber Die Casting
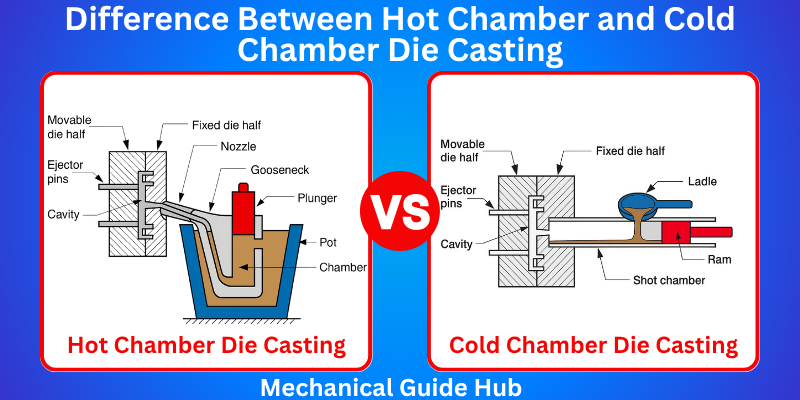
Hot Chamber Die Casting
- In hot chamber die casting, the metal melts inside the machine and is injected into the die using a piston.
- It operates faster since the metal is already molten and available within the machine.
- Operates at lower temperatures, resulting in less thermal stress and longer tool life.
- Often used to produce components that are small to medium in size.
- The system stays reliable longer due to its low-heat, low-stress environment.
- Economical for large-scale manufacturing of smaller parts.
- often gives a smoother surface finish due to precise and quick metal injection.
- Consumes less energy for each shot since metal is maintained in a ready-to-use state.
- It is more automation-friendly due to its faster cycle times and built-in melting system.
- typically require less aggressive die lubrication and have faster cooling cycles.
- Hot chamber setups may have lower initial costs for short-run production of small parts.
Cold Chamber Die Casting
- This method melts metal separately, moves it to a cooler chamber, and presses it into the mold cavity.
- It takes longer since the metal must be ladled in for each shot.
- It faces higher thermal loads and abrasion, causing faster wear and tear.
- This method works best for large, weighty, and complex-shaped components.
- Requires more care, as the high heat and pressure increase wear on parts.
- It is more energy-intensive but is necessary for stronger metals.
- May need extra surface treatment, especially with high-temp metals like aluminum.
- It consumes more energy since it relies on an external furnace and manual pouring.
- It requires manual or robotic ladling, making it less seamless to automate.
- need more robust cooling systems and die sprays due to higher metal temps.
- Cold chamber setups often involve higher equipment and tooling costs but are necessary for aluminum and other high-temp metals.
Conclusion
Now that you know the difference between hot chamber and cold chamber die casting, it’s easier to choose the right one for your project. Hot chamber casting works quickly with low-melting-point metals, whereas cold chamber casting is better suited for higher temperatures and larger components. Selecting the right process can improve efficiency, save costs, and give you better results.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks