Difference Between Rigid and Flexible Coupling
Published: 26 Jul 2025
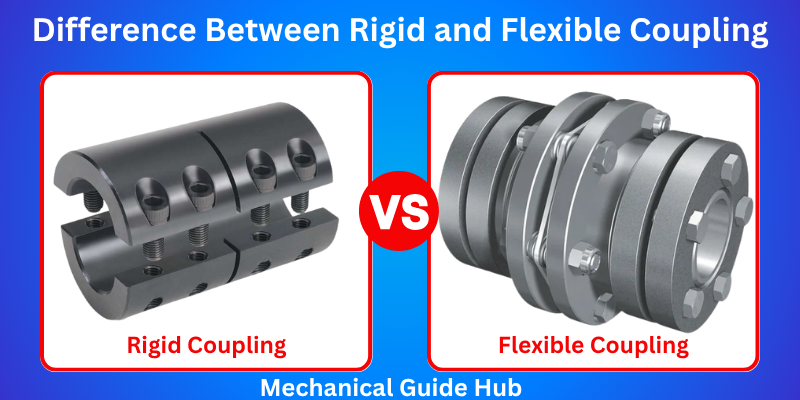
When building or maintaining a mechanical or piping system, choosing the right type of coupling is key. The difference between rigid and flexible couplings impacts everything from system performance to durability. Rigid couplings create solid, fixed connections with no movement, while flexible couplings can handle misalignment and vibrations. In this guide, we’ll break down the key differences to help you pick the best fit for your project.
Rigid vs Flexible Couplings: Key Differences
| Comparison | Rigid Coupling | Flexible Coupling |
| Design Purpose | Built for precise and fixed alignment between connected parts. | Designed to handle misalignment, vibration, and movement. |
| Flexibility | Offers no flexibility. Movement or vibration is not tolerated. | Designed to absorb vibrations and accommodate slight shaft alignment deviations. |
| Installation Requirements | Requires exact shaft alignment during installation. | Easy to install in systems where perfect alignment is difficult. |
| Torque Transmission | Provide maximum torque transmission with no energy loss. | Slightly reduces torque due to its ability to flex and dampen vibration. |
| Maintenance | Typically low-maintenance if alignment is accurate. | May require periodic inspection due to moving parts and potential wear. |
| Shock Absorption | Cannot absorb shocks or vibrations; may lead to system wear. | Excellent at absorbing mechanical shocks and vibrations. |
| Typical Applications | Ideal for systems with fixed components like pumps or gearboxes. | Suitable for dynamic systems like motors, compressors, or fire protection pipelines. |
| Material Composition | Usually made of metal (e.g., steel or aluminum). | Often includes rubber, elastomer, or composite materials to provide flexibility. |
| Cost | Budget-friendly due to the minimal and durable design. | Typically more costly because of its complex structure and flexible materials. |
| Noise Control | It can be noisy during operation due to its solid, inflexible structure. | Helps minimize operational noise by absorbing vibrations and energy. |
| Load Variations | Performs poorly under changing loads and is best suited to steady, consistent conditions. | Adapts more effectively to fluctuating loads, making it ideal for dynamic systems. |
| System Stress | Transfers stress directly, increasing strain on components. | Absorbs stress, reducing strain and wear. |
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between rigid and flexible couplings helps ensure your system runs smoothly and efficiently. Rigid couplings are perfect when alignment is critical and movement is minimal. Flexible couplings shine in dynamic setups where vibration, misalignment, or thermal expansion is common. Choosing the right one enhances performance and reduces wear and maintenance over time.
FAQs
Rigid couplings provide a solid connection with no allowance for misalignment, while flexible couplings can handle misalignment, vibration, and slight movement.
Flexible couplings reduce stress on components by absorbing misalignment, vibration, and thermal expansion, increasing system life and reliability.
Flexible couplings are used in systems with vibration, misalignment, or movement, like engines, pumps, blowers, and HVAC piping.
It’s called flexible because it allows for movement and flexibility between connected shafts or pipes, unlike rigid couplings.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks