What is Anvil Tool and Their Types
Published: 8 Aug 2025
An anvil is more than just a block of metal. It’s a timeless tool that has supported blacksmiths, farriers, and metalworkers for centuries. Known for its strength and durability, an anvil provides a solid surface for shaping, bending, and forging metal. Whether you’re a beginner learning the craft or a skilled artisan, understanding the parts, types, and uses of an anvil can help you choose the right one for your needs.
What is an Anvil?
An anvil is a heavy, flat-topped tool made from strong metals like steel or cast iron. It serves as a workbench for metal shaping, allowing you to hammer and bend pieces with precision. Its design hasn’t changed much over the years because it works perfectly for its purpose—providing a solid, shock-absorbing base for striking metal.
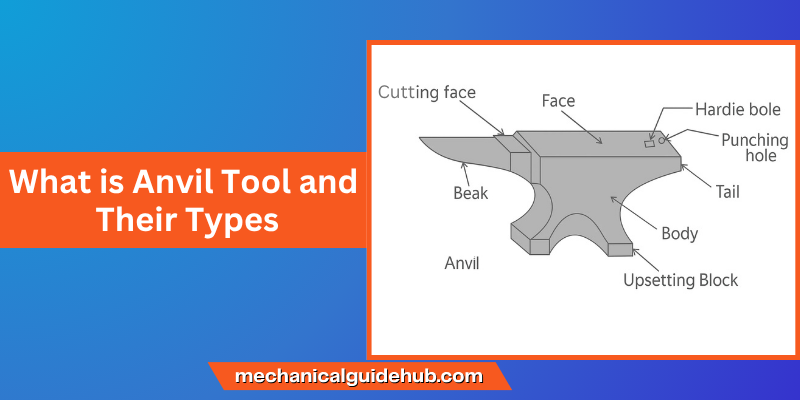
Anvil Parts and Functions
Horn
The horn is the rounded, cone-shaped end of the anvil. It’s mainly used for bending, curving, and shaping metal into smooth, rounded forms.
Face
The face is the flat working surface where most hammering happens. It’s hardened to resist dents and scratches.
Step
The step is a small ledge between the face and the horn. It’s used for cutting metal with a chisel or a hard tool.
Hardie Hole
The hardie hole is a square opening on the anvil’s face designed to secure hardy tools like cutters, bending fixtures, or other accessories, making it easier to perform precise shaping tasks.
Pritchel Hole
A round opening on the anvil, the pritchel hole is used for punching or drifting holes in metal while protecting the anvil’s face from damage.
Different Types of Anvils Used in Workshops
Blacksmith Anvils
These are the most common and versatile anvils. They typically have a broad face, a horn for shaping curves, and both hardy and pritchel holes. These anvils are widely used for general blacksmithing, shaping tasks, knife making, tool forging, and decorative ironwork.
Farrier Anvils
Designed for shaping horseshoes, farrier anvils have a longer, narrower horn and often include a clip horn for specialized shoe work. The edges are rounded to prevent damage to the horseshoe, and they are lighter and easier to transport than blacksmith’s anvils.
Bench Anvils
Small and lightweight, bench anvils are used for light-duty work on a workbench. They are great for hobbyists, small repairs, or working with soft metals like copper and brass.
Jeweler’s Anvils
Jeweler’s anvils are small and highly polished to prevent scratches on precious metals. They’re ideal for fine work like shaping rings, bracelets, or small metal components.
Stake Anvils
These have a long, pointed spike that fits into a base or bench. Stake anvils come in many shapes for different metal-forming needs, such as flattening, raising, or planishing sheet metal.
Cast Iron Anvils
Made from cast iron, these are cheaper and lighter but less durable than steel anvils. They are good for beginners or for light hammering tasks.
Colonial Anvils
A traditional style used in early blacksmithing, colonial anvils often have a simple block design and were handmade by early craftsmen.
Double Horn Anvils
These have a rounded horn on one side and a flat, square horn on the other, giving more shaping options for advanced metalwork.
Uses of Anvil in Workshop
- Forging metal into desired shapes
- Bending metal pieces
- Punching holes in metal
- Flattening metal surfaces
- Cutting metal parts
Essential for both heavy industrial work and small craft projects
How to Choose a Good Anvil?
When choosing an anvil, consider:
Material – Forged steel is best for durability.
Weight – A heavier anvil can absorb more of the hammer’s force, making each strike feel smoother and less tiring.
Surface – The face should be smooth and hardened.
Purpose – Choose a type that matches your work, whether it’s blacksmithing, farrier work, or jewelry making.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Anvil
Advantages
- Long-lasting and durable.
- Versatile for many types of metalwork.
- Stable and strong for heavy tasks.
Disadvantages
- Heavy and difficult to move.
- High-quality anvils can be expensive.
- Requires maintenance to prevent rust.
Conclusion
Anvils may look like simple blocks of metal, but their design, weight, and features make them powerful tools in metalworking. From blacksmiths to jewelers, professionals rely on them for precision and durability. By choosing the right anvil for your needs, you can work more efficiently and get better results.
FAQs
Anvil prices range from $50 for small bench anvils to over $1,000 for large forged steel anvils.
Forged steel anvils are the strongest due to their hardness and ability to resist wear.
Yes, it’s essential for shaping and forging metal, especially in blacksmithing and related trades.
Choose a weight that suits your work—small jobs need lighter anvils, while heavy forging requires larger ones.
Mostly forged steel or cast iron.
Blacksmiths, farriers, metalworkers, jewelers, and even some mechanics use anvils.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks



