Difference Between Disc Brake and Drum Brake
Published: 21 Jul 2025
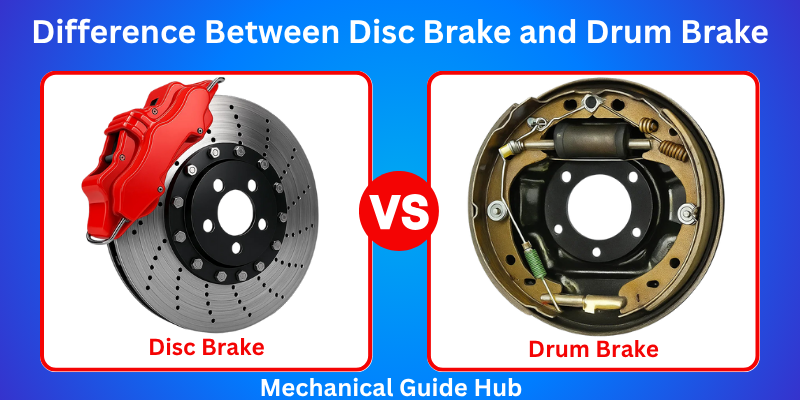
Brakes are a crucial safety component in any vehicle, helping you slow down or stop to avoid accidents. The majority of today’s vehicles rely on either drum brakes, disc brakes, or a hybrid setup of both. In this quick guide, we’ll explore the difference between disc brake and drum brake systems, how each one works, their benefits, and which might be the best fit for your car.
Disc Brakes vs Drum Brakes: Everything You Should Know
Disc Brake
- In disc brakes, hydraulic pressure forces the calipers to squeeze the pads against the disc, creating friction to slow the wheel.
- The system relies on calipers to press brake pads against a spinning rotor, producing friction to bring the wheel to a stop.
- The core components are the disc (rotor), caliper, brake pads, and the piston housed within the caliper.
- They provide better heat dissipation due to the open design and exposure to airflow.
- Offers stronger, quicker, and more reliable braking. Performs well in high-speed conditions.
- Exposed design allows water to escape easily. Maintains good performance in the rain.
- Easy to check and replace pads, with a low long-term cost.
- Durable but wears out faster under heavy use.
- Lighter and more compact.
- More expensive to manufacture and install.
- Can include a separate mechanism for the handbrakes.
- Complex mechanism with return springs and more components.
- Disc brakes can make a squeaking noise sometimes, especially if the pads are old or dirty.
- Standard on most front wheels; used on all wheels in luxury or performance cars.
Drum Brake
- In a drum brake system, hydraulic pressure pushes pistons in a wheel cylinder, forcing brake shoes outward to press against the rotating drum and create friction for braking.
- It uses brake shoes that press outward against the inside of a spinning drum to create braking force.
- The main parts of this system include the drum, brake shoes, cylinder, and springs.
- Retain more heat due to enclosed design, which can lead to reduced efficiency over time (brake fade).
- Provides moderate braking force. Can lose effectiveness when hot.
- The enclosed design can trap water, reducing braking efficiency.
- As a result of the use of springs and cylinders, it is more difficult and slower to service.
- Longer life in some heavy-duty vehicles, but may need regular cleaning.
- Heavier and bulkier due to internal components.
- Cheaper to produce and commonly used in budget or rear braking systems.
- Often integrated with the parking brake system.
- Simple design, fewer moving parts.
- Drum brakes are quieter.
- Commonly used in the rear wheels of budget-friendly passenger cars, trucks, and trailers.
Conclusion
Choosing between disc brakes and drum brakes involves weighing your priorities—performance, cost, durability, and maintenance. Disc brakes provide top-tier stopping power and quick response, ideal for performance-focused or safety-conscious drivers. On the other hand, drum brakes offer a budget-friendly and dependable solution under standard driving conditions.
By understanding the differences between these braking systems, you can make a confident, informed choice that aligns with your needs and keeps your driving experience safe and efficient.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

