Velox Boiler Construction, Working and Applications
Published: 23 Oct 2025
The Velox Boiler is a high-pressure, forced-circulation water tube boiler widely used in the modern steam power plants and gas turbine industries. This boiler stands out for its unique working principle, which increases the rate of heat transfer by allowing gases to flow at velocities greater than the speed of sound. This not only boosts the steam generation rate but also ensures high efficiency without increasing the boiler’s physical size. Compact, efficient, and powerful, the Velox Boiler is a remarkable example of innovation in steam generation technology.
What is Velox Boiler
A Velox Boiler is a type of forced circulation water-tube boiler that uses pressurized combustion and supersonic gas flow to maximize heat transfer. The boiler uses a gas turbine-driven air compressor to compress air before combustion. When the fuel burns in the combustion chamber, it produces high-velocity flue gases that move faster than the speed of sound. This high gas velocity transfers more heat to the water inside the tubes, increasing the steam generation rate.
With a thermal efficiency of about 90–95%, the Velox Boiler is known for its compact design, rapid steam production, and suitability for high-pressure applications, especially in gas turbine systems.
Construction of Velox Boiler
The Velox Boiler is made up of several essential components arranged in a compact layout to ensure efficient operation. The main parts are:
Velox Boiler Diagram
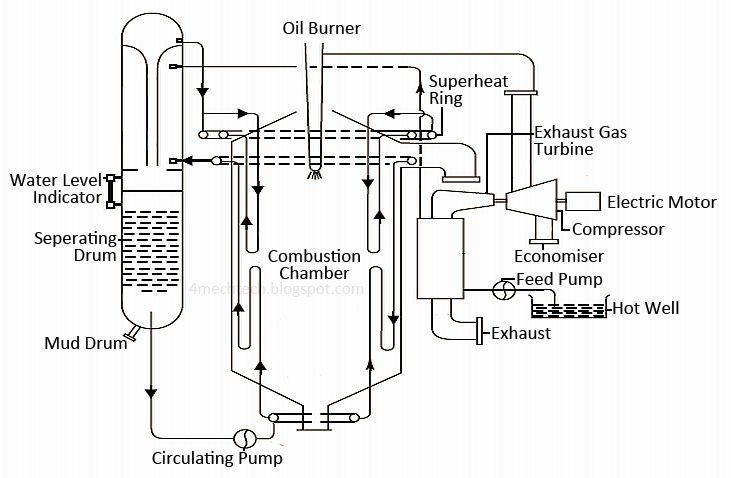
Feed Pump: Feeds water into the economizer at high pressure.
Economizer: Preheats the feed water using exhaust flue gases before it enters the evaporator section.
Water Circulating Pump: Forces the preheated water through evaporator tubes multiple times to ensure rapid heating.
Combustion Chamber: A pressurized chamber where fuel and compressed air mix and burn, generating high-temperature flue gases.
Gas Turbine: Converts some of the flue gas energy into mechanical energy to drive the axial compressor.
Axial Compressor: Compresses the incoming air before sending it to the combustion chamber for efficient combustion.
Steam Separator: Separates steam from the water-steam mixture before sending the steam to the superheater.
Superheater: Heats the saturated steam further to produce superheated steam for industrial use.
All components are designed to work together in a closed-loop system to ensure efficient and continuous steam production.
Working of Velox Boiler
The Velox Boiler works on the principle that when gas velocity exceeds the velocity of sound, the rate of heat transfer increases significantly. The working process can be explained step by step:
The feed pump supplies water to the economizer, where it is preheated using exhaust gases from the turbine. This preheated water then moves to the water circulating pump.
The circulating pump pushes the warm water through the evaporator tubes located around the combustion chamber. The water circulates through these tubes 15–20 times at high speed, enhancing the heat absorption rate.
Simultaneously, a gas turbine drives the axial air compressor, which compresses air and sends it into the combustion chamber. Inside this chamber, the compressed air mixes with fuel and burns at high pressure, producing flue gases that reach supersonic velocities.
The flue gases pass through fire tubes surrounded by evaporator tubes containing water. The high-speed flue gases transfer heat rapidly to the water, forming a steam-water mixture.
The mixture moves to the steam separator, which separates dry steam from water. The separated steam flows to the superheater, where it gains additional heat from flue gases to become superheated steam.
After transferring heat in the superheater, the flue gases pass through the economizer, heating the incoming feed water before being released into the atmosphere.
This entire process results in rapid and efficient steam generation suitable for industrial power applications.
Specification of Velox Boiler
Type: Forced circulation, water tube boiler
Working Pressure: High pressure (up to 100 bar)
Steam Generation Capacity: Up to 100 tonnes/hour
Thermal Efficiency: 90–95%
Fuel Used: Gas
Air Supply: Axial compressor driven by a gas turbine
Circulation Type: Forced circulation
Superheater: Present
Economizer: Present
Application of Velox Boiler
The Velox Boiler is widely used in industries that demand high efficiency and a compact design. Common applications include:
- Gas turbine power plants
- Industrial steam generation units
- Chemical and Petrochemical industries
- Marine propulsion systems
- Industrial plants with limited space but high steam requirements
Advantages of Velox Boiler
- Compact design requires less space than other boilers.
- Can start quickly and operate efficiently under varying loads.
- Excellent flexibility and ease of operation.
- High thermal efficiency (about 90–95%).
- High rate of heat transfer due to supersonic gas velocity.
- Fully automatic control system ensures consistent performance.
Disadvantages of Velox Boiler
- High initial installation and maintenance costs.
- Limited size — maximum output is around 100 tonnes/hour.
- Requires external power or a gas turbine to run the air compressor.
- Complex design and maintenance compared to conventional boilers.
Conclusion
The Velox Boiler is a brilliant example of engineering innovation, combining compact design, high efficiency, and advanced thermodynamic principles. Its unique feature of utilizing supersonic gas flow allows it to achieve exceptional heat transfer and steam generation rates without expanding its size. Despite some limitations, it remains a top choice in gas turbine plants and industrial steam systems where performance and efficiency are paramount.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks