What is Piston: Parts, Functions, Types, and Working Explained
Published: 7 Oct 2025
The piston is one of the most crucial components of an internal combustion engine. It moves up and down inside the cylinder, converting the force of expanding gases into the mechanical power that drives your vehicle. Without a piston, no energy from fuel combustion could be transformed into motion. In this article, we’ll explore what a piston is, its parts, how it works, and its types in a simple, easy-to-understand way.
What is Piston
A piston is a cylindrical-shaped metallic component that fits perfectly inside the engine cylinder. It forms the heart of the combustion process, as it moves up and down during every cycle of operation. Pistons are generally made of lightweight aluminum alloys because they can resist extreme heat, high pressure, and wear while maintaining efficiency and speed. The piston connects to the crankshaft through a connecting rod, transforming linear motion into rotary motion.
Piston Parts and Their Functions
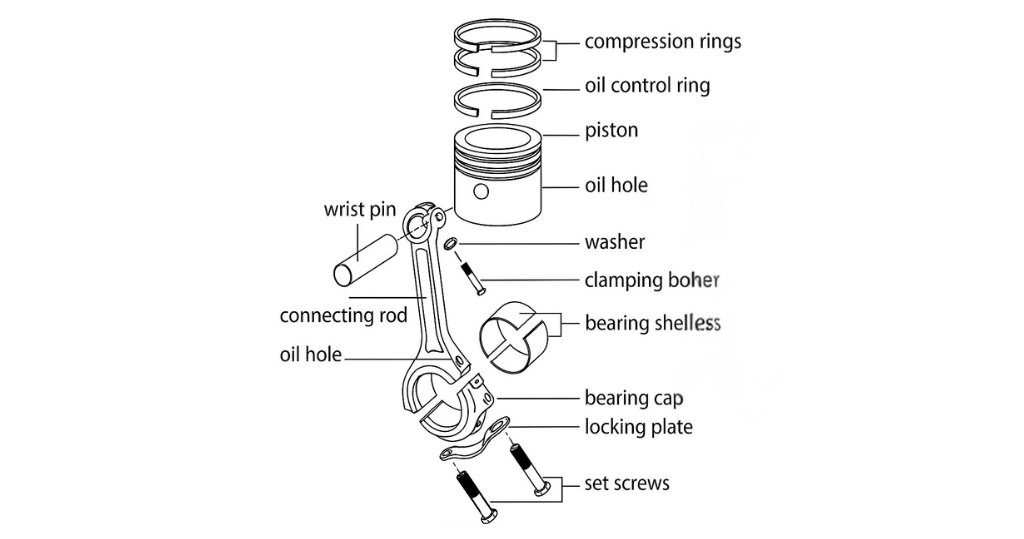
A piston is made up of several intricate parts, each with a specific purpose that ensures the engine runs smoothly and efficiently. Below are all the essential piston parts and their detailed functions:
1. Piston Head (Crown)
The piston head, also called the crown, is the top surface of the piston that comes in direct contact with the burning gases. It endures extremely high temperatures and pressures during combustion and helps transfer the generated force evenly down to the connecting rod.
2. Piston Rings
These are metal rings fitted into grooves on the outer surface of the piston. Piston rings provide a gas-tight seal between the piston and the cylinder wall, preventing gas leakage, controlling oil consumption, and transferring heat from the piston to the cylinder wall.
3. Compression Rings
Located at the top groove, compression rings seal the combustion chamber to prevent gas blow-by. They ensure the full force of combustion is used to push the piston downward, maximizing engine power and fuel efficiency.
4. Wiper Ring (Intermediate Ring)
The wiper ring is placed below the compression ring and helps remove excess oil from the cylinder walls. It also adds an extra sealing layer, preventing leftover gases from entering the crankcase and ensuring smooth piston motion.
5. Oil Control Ring
Positioned at the lowest groove, this ring regulates the oil film on the cylinder wall. It scrapes excess oil back into the crankcase, preventing it from burning inside the combustion chamber and keeping emissions low.
6. Ring Grooves
These are precisely machined circular slots around the piston where the piston rings are installed. They allow the rings to move slightly during operation, ensuring optimal sealing, lubrication, and heat transfer.
7. Ring Lands
The areas between two ring grooves are called ring lands. They provide support to the rings, prevent excessive movement, and maintain the right spacing to avoid piston failure under high stress.
8. Piston Skirt
The skirt is the cylindrical portion below the ring section. It guides the piston inside the cylinder, reducing side thrust and friction. The skirt helps maintain the alignment of the piston during reciprocating motions.
9. Piston Pin (Gudgeon Pin or Wrist Pin)
This is a hardened hollow pin that connects the piston to the connecting rod. It allows the piston to pivot smoothly during each stroke and withstands the heavy loads created by combustion.
10. Piston Pin Bore
The piston pin bore is the hole machined through the piston bosses where the Gudgeon pin fits. It ensures accurate alignment between the piston and the connecting rod, allowing efficient motion transfer.
11. Connecting Rod
The connecting rod links the piston to the crankshaft and transmits the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion. Made of forged steel or aluminum, it must withstand enormous stresses during every stroke.
12. Connecting Rod Bolt and Cap
The connecting rod bolt and cap hold the big end of the connecting rod firmly around the crankshaft journal. This secure connection ensures stability and strength during high-speed rotations.
13. Piston Bearings
Bearings are placed at the connecting points of the piston assembly to minimize friction and wear. They provide smooth rotation, support high loads, and help maintain precise alignment between the piston and crankshaft.
14. Piston Boss
These are reinforced areas on the inner side of the piston that house the piston pin bore. The bosses provide strength and stability to hold the gudgeon pin firmly during high-pressure combustion cycles.
15. Piston Ring Expander
The expander is a small spring component located behind the oil control ring. It pushes the ring outward to maintain constant contact with the cylinder wall, improving oil control and sealing efficiency.
16. Cooling Channels (in some pistons)
Some modern pistons include oil cooling channels that help dissipate heat from the crown area. These channels allow oil to circulate and absorb excess heat, preventing piston overheating and deformation.
Function of Piston
The main function of a piston is to convert the energy produced by the combustion of fuel and air into mechanical motion. As combustion occurs, high-pressure gases push the piston downward, turning the crankshaft.
Other key functions include:
- Compressing the air-fuel mixture before ignition.
- Expelling exhaust gases after combustion.
- Maintain proper sealing of the combustion chamber.
- Transferring heat to the cylinder wall for cooling.
How Piston Rings Work?
Piston rings are responsible for sealing the gap between the piston and cylinder wall. During operation, the compression ring seals the combustion gases, the wiper ring controls leftover oil, and the oil control ring removes excess oil. Together, they prevent leakage, reduce friction, and maintain efficient lubrication — all while transferring heat from the piston to the cylinder.
How Does a Piston Work?
A piston works through a continuous four-stroke cycle — intake, compression, power, and exhaust.
Intake Stroke: The piston moves down, drawing in an air-fuel mixture.
Compression Stroke: It moves up, compressing the mixture for ignition.
Power Stroke: The mixture ignites, forcing the piston downward.
Exhaust Stroke: The piston moves up again, pushing out the burnt gases.
This process repeats hundreds of times per second to keep the engine running efficiently.
Types of Piston

1. Dish Pistons
Dish pistons have a concave or bowl-shaped top. This design helps reduce the compression ratio and prevents engine knocking. These pistons are often used in turbocharged or supercharged engines because they manage high-pressure combustion safely. The dish shape also helps improve air-fuel mixing for better performance.
2. Flat-Top Pistons
Flat-top pistons have a simple, flat head surface. They provide a balanced compression ratio and efficient fuel burn. Because of their design, they are commonly used in standard car engines. They deliver a good mix of power, fuel efficiency, and durability, making them suitable for everyday use.
3. Dome Pistons
Dome pistons have a raised or dome-shaped top. This increases the compression ratio, resulting in more power output. These are used in high-performance and racing engines where maximum power is needed. However, they can sometimes cause uneven combustion if not properly designed, so they require precise tuning.
Conclusion
The piston is the powerhouse of any internal combustion engine. From converting explosive energy into motion to maintaining seals and heat transfer, it ensures your engine runs smoothly. Understand its parts, functions, and types helps you appreciate its importance and keep your engine performing at its best.
FAQs
Piston का मतलब होता है “पिस्टन” — यह इंजन का वह हिस्सा है जो सिलेंडर में ऊपर-नीचे चलता है और ईंधन की शक्ति को यांत्रिक शक्ति में बदलता है।
Piston price varies depending on engine type and size. Generally, small engine pistons cost between ₹500–₹5000, while high-performance or car pistons can range from ₹7000–₹20,000.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks


