42 Basic Parts of Motorcycle & Their Functions with Pictures
Published: 6 Aug 2025
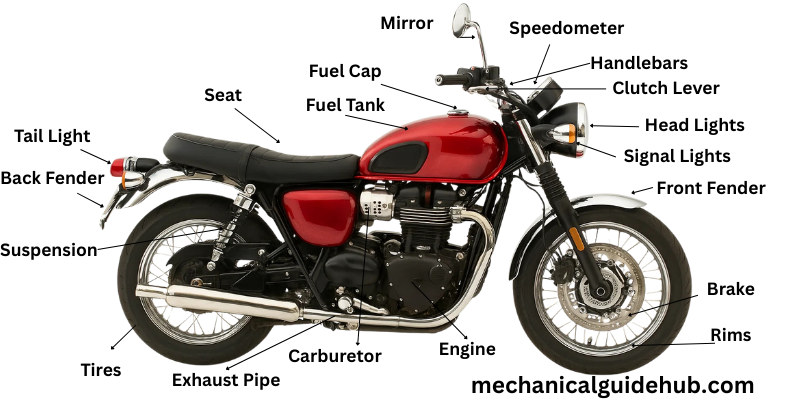
A motorcycle works because all its parts do specific jobs. Knowing what each part does helps you ride better and fix minor issues. Let’s look at each one.
List of Motorcycle Parts and their Functions
1. Engine
The engine burns fuel to power your bike. It creates the energy that makes the bike move.
2. Transmission
This part carries power from the engine to the wheels. It also lets you shift between speeds.
3. Frame
The frame holds all the parts together. It gives the bike its shape and structure.
4. Carburetor
The carburetor mixes air and fuel. This mixture enters the engine for combustion.
5. Clutch Lever
On the left handlebar, the clutch lever disconnects the engine from the wheel. It is used to change gears by pulling it.
6. Front Brake Lever
This lever is on the right handlebar. You squeeze it to stop the front wheel.
7. Rear Brake Lever
Located by your right foot, the rear brake lever helps to slow down the back wheel.
8. Throttle
Twist the throttle on the right handle. It increases fuel flow to fasten the bike.
9. Gear Shifter
The gear shifter is used with your left foot to change gears as your speed increases or decreases.
10. Horn
A button for alerting others. It’s quick and important for safety.
11. Pegs
Foot pegs support your feet while riding. They help maintain balance.
12. Engine Guards
Metal bars around the engine. They protect it if the bike falls.
13. Signal Lights
Flashing lights that show left or right turns. They keep you visible to others.
14. Headlights
The front lamp that lights the road ahead. They also make you visible at night.
15. Tail Light
Rear-facing light that turns on when you brake or ride in low light.
16. Mirrors
Mounted on the handlebars. They let you see behind without turning your head.
17. Start Button
A push button is on the right handlebar. It starts the engine when pressed.
18. Choke
The choke helps start the engine in cold weather by adding more fuel to the mix.
19. Ignition Key Switch
The ignition key switch turns the bike’s power on and off.
20. Fuel Tank
Stores fuel for the engine. It sits just above the engine and often has knee grips.
21. Tires
Rubber coverings that touch the road. They give you grip and help you brake safely.
22. Rims
Metal rings that hold the tires. They keep the wheels sturdy and round.
23. Brakes
Two systems—front and rear—that slow or stop the bike when applied.
24. Brake Cable
Connects the brake lever to the brake mechanism. Transfers the force you apply.
25. Kickstand
A metal stand that keeps your bike upright when parked. Always tuck it up before riding.
26. Suspension
Front forks and rear shocks absorb bumps. They make your ride smooth and comfortable.
27. Exhaust/Pipe
Channels exhaust gases away from the engine. It also reduces sound.
28. Seat
Where the rider (and maybe a passenger) sits. It’s padded for comfort.
29. Spark Plugs
Small devices that create sparks. They ignite the fuel-air mix in the engine.
30. Stator
Generates electricity while the engine is running. It keeps the battery charged.
31. Battery
Stores electrical power. Powers lights, horn, and starter when the engine is off.
32. Dashboard
Displays speed, fuel, and warning lights. Let the rider monitor the bike status.
33. Tachometer
Shows engine RPM. Helps you know when to shift gears.
34. Speedometer
Displays how fast you’re traveling. Helps you stay within safe speed limits.
35. Storage
Built-in spaces like under the seat or saddlebag areas. Useful for small items or tools.
36. Handlebars
It allows you to steer the bike. They also hold all the control switches and levers.
37. Safety Bar
Also called a crash guard. It protects the bike and the rider during a fall.
38. Sprockets
Toothed wheels connected by a chain. They transmit power from the engine to the rear wheel.
39. Fuel Cap
Seals the fuel tank. Remove it to refill and securely replace it after.
40. Tube
A rubber inner layer is inside some tires. Holds the air and supports tire pressure.
41. Front Fender
A cover above the front wheel. Stops mud and water from splashing up.
42. Triple Tree
Connects the front fork tubes to the handlebars. It supports steering and front suspension.
Conclusion
These motorcycle parts each serve a clear purpose. By knowing what they do, you become a smarter, safer rider. You can spot issues early and ride confidently.
FAQs
CC stands for cubic centimeters. It measures the engine’s size or capacity. Higher CC means more power; lower CC gives better fuel efficiency.
There are five main types of motorcycle engines:
Single-cylinder
Parallel-twin
V-twin
Inline-four
Boxer (flat-twin)
Each type offers different power, performance, and efficiency.
A motorcycle has over 50 key parts, including the engine, transmission, wheels, brakes, frame, suspension, lights, and control components. Each part plays an important role in performance and safety.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks



