Lamont Boiler Construction Working and Applications
Published: 18 Oct 2025
A Lamont boiler is one of the most efficient and reliable water-tube boilers used for power generation. It is widely known for its forced circulation system that helps in quick steam production. This boiler is mainly used in power plants to generate electricity. Understanding its parts, working, and specifications can help you know why it is one of the most popular high-pressure boilers in modern industries.
What is a Lamont Boiler
A Lamont boiler is a high-pressure, forced-circulation, water-tube boiler with an internally fired furnace. It uses a centrifugal pump to circulate water inside small-diameter tubes. These tubes are surrounded by hot flue gases produced in the furnace. The boiler works at high pressure, around 170 bar, and produces steam efficiently. It was first introduced in 1925 and is named after Walter Douglas LaMont, who developed the concept of forced circulation in boilers. This design allows faster heat transfer, better performance, and continuous steam generation.
Lamont Boiler Diagram
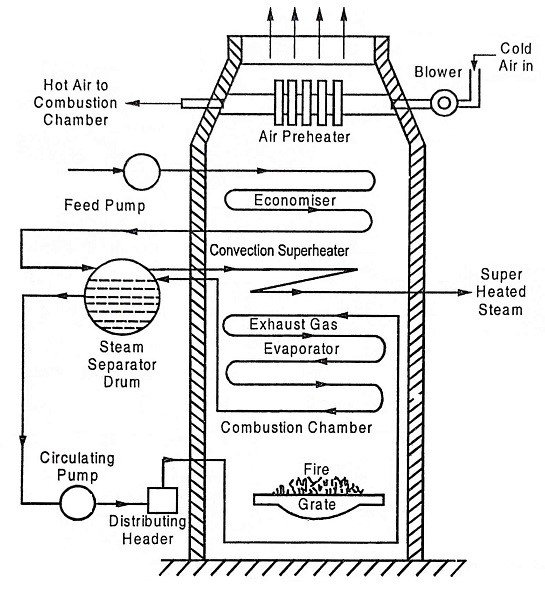
Construction of Lamont Boiler
The construction of a Lamont boiler is simple but efficient. It mainly includes the following parts:
Feed Pump: It supplies water from the hot well to the economizer.
Economizer: Preheats the feed water using leftover heat from flue gases, improving efficiency.
Centrifugal Pump: Circulates water continuously through the tubes to maintain forced circulation.
Steam Separating Drum: Separates steam from water before sending it to the superheater.
Superheater: Converts saturated steam into dry, superheated steam for turbine use.
Radiant Evaporator: Heats the water through radiation from the furnace.
Convective Evaporator: Uses convection to complete the steam formation process.
Air Preheater: Preheats the air before it enters the furnace to improve combustion efficiency.
Blower: Supplies air to the air preheater and then to the furnace for combustion.
Combustion Chamber: Burns fuel (usually coal) to generate hot flue gases for heating the tubes.
All of these parts work together to ensure smooth operation and efficient steam production.
Working of Lamont Boiler
The Lamont boiler operates on the principle of forced water circulation using a pump. Water from the feed pump enters the economizer, where it absorbs heat from the flue gases. From the economizer, the heated water moves to the steam separating drum. A centrifugal pump then sends this water through the small water tubes located in the furnace area.
As the flue gases surround these tubes, heat transfers to the water, converting it into steam. The mixture of steam and water returns to the separating drum. Here, steam separates from water. The steam then passes through the superheater, where its temperature increases further to become superheated steam. This steam is finally sent to turbines to produce electricity. The leftover water recirculates back through the system, maintaining continuous operation.
Specification of Lamont Boiler
Here are some important specifications of the Lamont boiler:
Type: Water tube, forced circulation boiler
Working Pressure: Around 170 bar
Steam Generation Capacity: Up to 50,000 kg/hour
Temperature: About 773 K
Efficiency: High due to the economizer and air preheater
Fuel Used: Coal or similar solid fuels
These specifications make it a strong and efficient boiler choice for industrial and power plant operations.
Application of Lamont Boiler
Lamont boilers are widely used in several industries because of their efficiency and reliability. Common applications include:
Power Plants: For generating steam to drive turbines and produce electricity.
Sugar Mills: To provide process steam for various operations.
Chemical Industries: For heating and processing requirements.
Marine Applications: In ships that require compact, high-pressure boilers.
Its quick start and high steam generation rate make it ideal for industries needing consistent steam supply.
Advantages of Lamont Boiler
- Simple design and easy to start.
- High heat transfer rate and efficiency.
- Produces up to 50 tons of steam per hour.
- It can be easily reassembled with natural circulation systems.
- Flexible operation and suitable for high-pressure applications.
Disadvantages of Lamont Boiler
- Bubble formation occurs on the inner surface of tubes, reducing heat transfer efficiency.
- Maintenance can be slightly complex due to the forced circulation system.
- Requires a continuous power supply for the centrifugal pump.
Conclusion
The Lamont boiler is one of the most practical and efficient boilers used in power generation. Its forced circulation system, high-pressure capacity, and fast steam generation make it a popular choice in industries and power plants. Although it faces minor drawbacks like bubble formation, its advantages outweigh its limitations. Overall, the Lamont boiler remains an essential part of modern thermal engineering and continues to play a major role in industrial steam production.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks


