Kaplan Turbine: Components, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages & Applications
Published: 26 Dec 2025
In this article, we will discuss what a Kaplan Turbine is, its main components, working, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. The Kaplan Turbine is one of the most widely used turbines in hydroelectric power plants, especially in areas with low head and high water flow. Let’s explore it in a simple and easy-to-understand way.
What is Kaplan Turbine?
A Kaplan Turbine is an axial-flow reaction turbine developed by Viktor Kaplan in 1913. It is designed to operate efficiently in low-head and high-discharge water conditions, making it ideal for river-based hydropower stations. Its main feature is its adjustable runner blades and guide vanes, which automatically change their angle to maintain maximum efficiency even when water flow varies.
Main Components of Kaplan Turbine
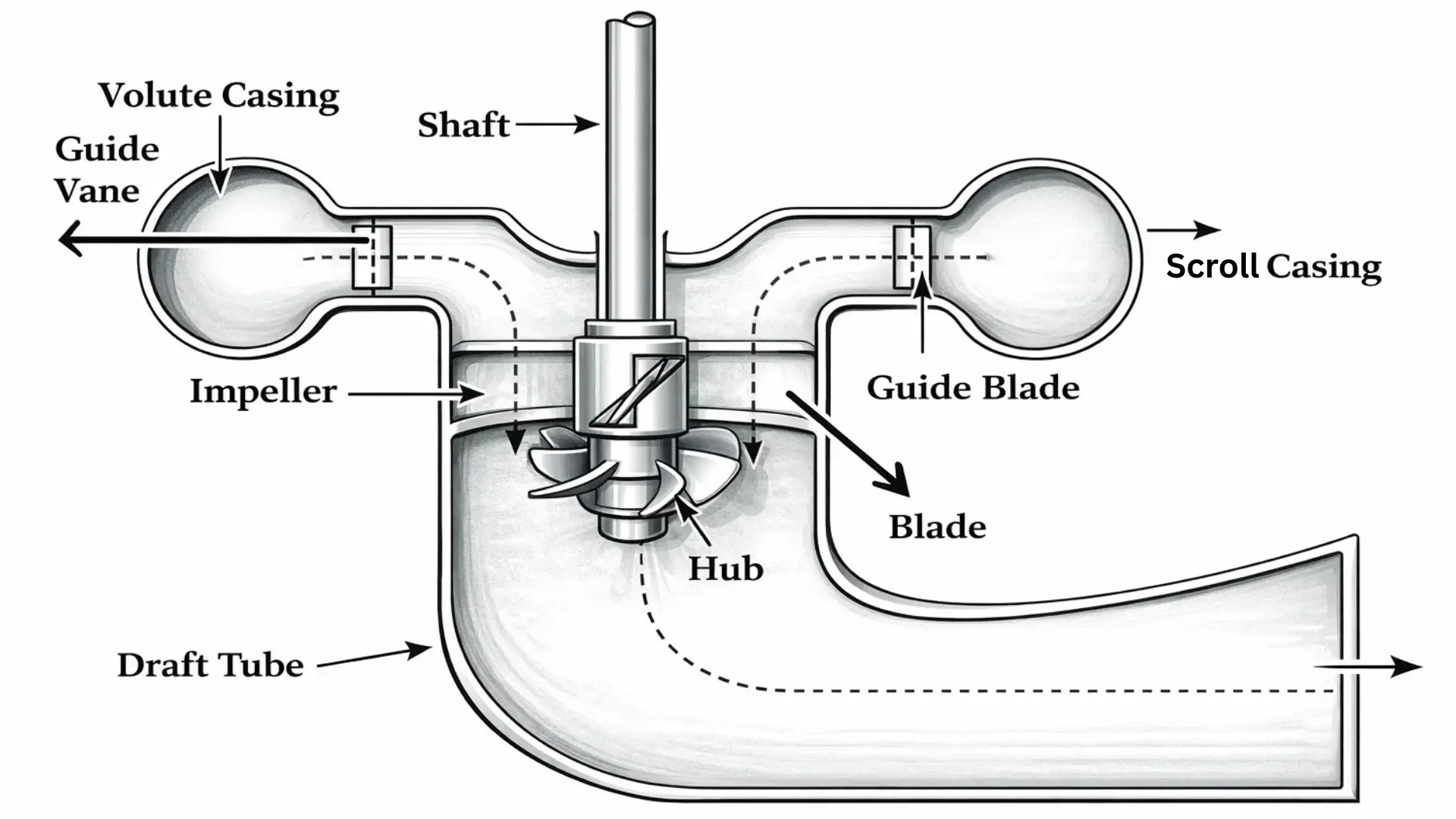
Here are some of the main parts of a Kaplan Turbine:
1. Scroll Casing
The scroll casing (or spiral casing) is a curved, gradually narrowing housing that distributes water uniformly around the turbine. It maintains the pressure of water as it moves toward the guide vanes.
2. Guide Vane Mechanism
Guide vanes regulate the flow of water entering the runner. They open or close depending on power demand. When water passes through them, they direct it at the proper angle toward the runner blades, increasing turbine efficiency.
3. Draft Tube
The draft tube is a gradually expanding tube fixed at the exit of the runner. It converts the remaining kinetic energy of water into pressure energy and safely leads it to the tail race. It also helps prevent energy loss and supports smoother water discharge.
4. Runner Blades
The runner blades are the most important part of the Kaplan turbine. These blades are adjustable and shaped similarly to a propeller. As water strikes them axially, they rotate the runner and drive the turbine shaft. Their pitch changes automatically according to water flow conditions.
5. Turbine Shaft
The turbine shaft is connected to the runner on one end and to the generator on the other. When the runner rotates, the shaft also rotates, which ultimately helps produce electricity. It is made of strong, heat-resistant materials because it operates at high speeds.
6. Tail Race
The tail race is the channel that carries used water from the turbine back to the river or reservoir. It ensures smooth discharge and maintains the necessary pressure difference for turbine operation.
Working of Kaplan Turbine
The Kaplan turbine works on the reaction principle and an axial flow mechanism. Here’s how it operates:
- Water from the penstock enters the scroll casing, which distributes it evenly.
- The guide vanes adjust their angle to control the direction and amount of water entering the runner.
- Water flows axially and hits the runner blades, causing them to rotate.
- The rotation of the runner turns the turbine shaft, which is connected to the generator.
- The generator produces electricity as the shaft spins.
- After delivering energy, water leaves through the draft tube, where its pressure is recovered.
- Finally, water is safely discharged into the tail race.
Because both the guide vanes and the runner blades are adjustable, the turbine maintains high efficiency even when the water flow changes.
Advantages of Kaplan Turbine
Here are some easy-to-understand benefits:
- It gives high efficiency at low and medium water heads.
- It works well even when the water flow changes.
- It has adjustable blades for better performance.
- Kaplan turbines have a compact design and are easy to install.
- It supports clean and renewable energy.
- It has a low environmental impact compared to other systems
Disadvantages of Kaplan Turbine
Here are some limitations you should know:
- It is sensitive to dirt and debris in water.
- It can face issues like cavitation and turbulence.
- Blade adjustment systems are complex and need skilled workers.
- It is not suitable for high-head sites.
- It has a high installation cost.
- It may affect fish movement and aquatic life if not managed properly.
Application of Kaplan Turbine
Kaplan turbines are commonly used in:
- Hydroelectric power plants, especially river-based systems
- Low head water resources with high flow rates
- Small and medium hydropower stations
- Renewable energy projects where water levels frequently vary
- Sites requiring compact yet highly efficient turbine systems
Conclusion
In conclusion, in this article, we covered what a Kaplan turbine is, its main components, working, advantages, disadvantages, and applications in detail. We hope you find this helpful. Feel free to share it with your friends.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

