Different Types of Belt Drives in Mechanical Engineering
Published: 4 Oct 2025
Belt drives are a fundamental component in mechanical systems, providing a simple and effective way to transfer power between rotating shafts. From industrial machines to everyday appliances, belt drives are widely used due to their reliability, low cost, and ease of maintenance. Understanding how they work, the types available, and their applications is essential for engineers, students, and machine operators alike.
What Is a Belt Drive?
A belt drive is a power transmission system that uses a continuous flexible belt looped over pulleys to transmit rotational motion from one shaft to another. The belt is typically made of strong yet flexible materials, allowing it to transfer power efficiently while accommodating small misalignments between shafts. Belt drives are especially popular in applications requiring smooth, quiet operation and moderate speed and power transmission.
Different Types of Belt Drives
1. Open Belt Drive
In an open belt drive, the driver and driven shafts rotate in the same direction. The belt runs over parallel pulleys, with one side being tight and the other slack. This setup is simple, cost-effective, and widely used in light to medium power transmission. Open belt drives are common in machinery where shafts are aligned and speed ratios are moderate.
2. Crossed or Closed Belt Drive
Crossed belt drives, also called closed belt drives, transmit more power than open belt drives but are prone to wear due to belt rubbing. The shafts rotate in opposite directions, and the belt forms a figure-eight pattern between the pulleys. This type requires careful tensioning and slower operation to reduce friction and increase belt life. It is typically used where reversing the direction of rotation is required.
3. Fast and Loose Pulley Drive
This drive system uses two pulleys on a single shaft: a fast pulley that is fixed and transmits power, and a loose pulley that rotates freely. It allows individual machines to stop without turning off the main power source. Fast and loose pulleys are commonly used in workshops with multiple machines driven from one engine or motor. The setup provides flexibility while maintaining simplicity.
4. Stepped Cone Pulley Drive
Stepped cone pulleys, also called speed cones, consist of multiple pulleys of varying diameters mounted adjacent to each other. By moving the belt to a different step, the speed of the driven shaft can be easily changed. This type is ideal for machines like lathes and milling machines, where frequent speed adjustment is required. It provides smooth transitions between speeds without complex mechanisms.
5. Jockey Pulley Drive
A jockey pulley, also known as an idler pulley, is used to increase the belt’s contact angle and tension in an open belt drive. By doing so, it improves grip and enhances the drive’s power transmission capacity. The pulley is usually mounted near the smaller pulley and on the slack side of the belt. Jockey pulleys are often found in industrial and automotive applications where high efficiency and reduced slippage are essential.
Application of Belt Drive
Belt drives are versatile and widely used in many industries:
- Lathes, milling machines, and drilling machines.
- Material handling in factories and warehouses.
- Timing belts, alternator drives, and fan belts.
- Threshers, harvesters, and other farm machinery.
- Washing machines, vacuum cleaners, and fans.
- Spinning, weaving, and processing machines.
Advantages of Belt Drives
- Belt drives offer several benefits that make them ideal for many applications:
- Simple construction and easy to install.
- Cost-effective and low maintenance.
- Smooth and quiet operation.
- Flexible design, allowing long-distance shaft connections.
- Shock absorption capability reduces wear on other components.
- Adjustable speed using stepped pulleys.
Disadvantages of Belt Drives
- Despite their advantages, belt drives also have some limitations:
- Limited power transmission capacity compared to chain or gear drives.
- Slipping and creep can reduce efficiency.
- Faster wear and tear under heavy loads.
- Not suitable for very high-speed operations.
- Performance may drop in extreme temperatures or high humidity.
- The velocity ratio may not be constant due to belt slip.
Types of Belt
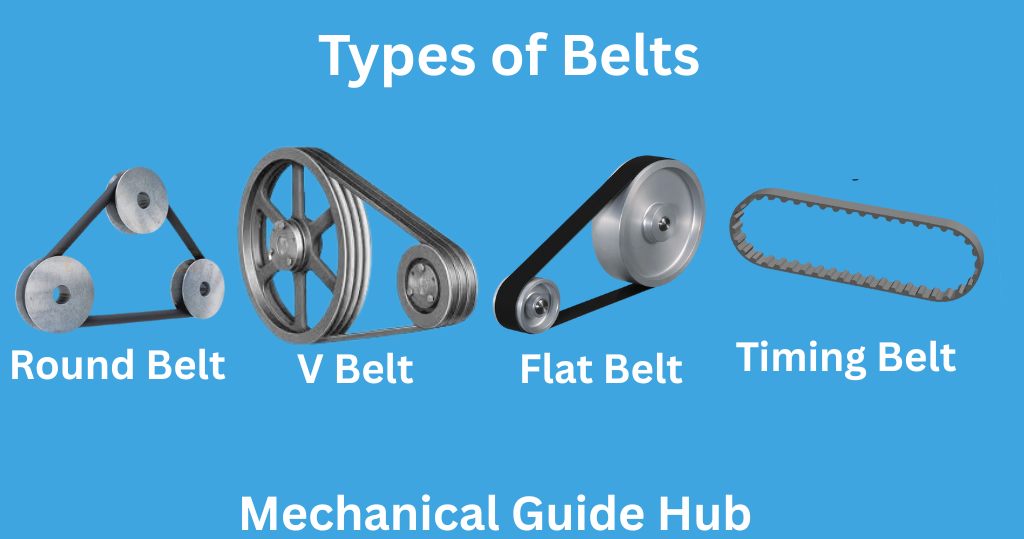
1. Round Belts
Round belts have a circular cross-section and are generally made of rubber. They are mainly used for light loads and motion transmission, such as sewing machines or vacuum cleaners. Their flexibility allows easy guidance in multiple directions using simple pulleys.
2. V Belts
V-belts have a trapezoidal cross-section that fits into a V-shaped pulley groove. This design increases friction and prevents slipping, allowing higher power transmission with less tension. V-belts are widely used in industrial machinery and automobile engines due to their reliability and efficiency.
3. Flat Belts
Flat belts have a rectangular cross-section and are suitable for long-distance power transmission with moderate power. They run quietly, have high efficiency, and can handle high speeds. Early flat belts were made of leather, while modern versions use synthetic materials for better durability.
4. Timing/Toothed Belts
Timing belts have teeth on the inner side that fit into grooves on the pulley, ensuring positive, slip-free engagement. They are used where precise synchronization between shafts is required, such as in car engines, printers, and 3D printers. Timing belts provide accurate motion and reliable power transfer.
Conclusion
Belt drives remain an essential part of mechanical systems due to their simplicity, efficiency, and versatility. Whether in industrial machines, automobiles, or household appliances, the right belt drive can ensure smooth, quiet, and reliable operation. Understanding the types of belt drives, their advantages, limitations, and appropriate belt selection is key to achieving optimal performance in any application.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

