Diesel Power Plant: Components, Working, Applications, Advantages & Disadvantages
Published: 19 Nov 2025
Diesel power plants are one of the most reliable sources of electricity. They are widely used to produce power where a continuous supply of electricity is needed, especially in remote areas. Do you know that diesel power plants can start quickly and provide electricity even during emergencies? In this article, we will explore what a diesel power plant is, how it works, its main components, applications, advantages, and disadvantages.
What is a Diesel Power Plant?
A Diesel Power Plant is a facility that generates electricity using diesel engines as the main driving force. It converts chemical energy in diesel fuel into mechanical energy and then into electrical energy. Diesel power plants are commonly used for backup power, remote areas, and industries that require continuous electricity. They are also called diesel generating stations or diesel gensets.
Essential Components of Diesel Power Plant
A diesel power plant consists of several interconnected components that ensure smooth and efficient electricity generation:
Diesel Power Plant Diagram
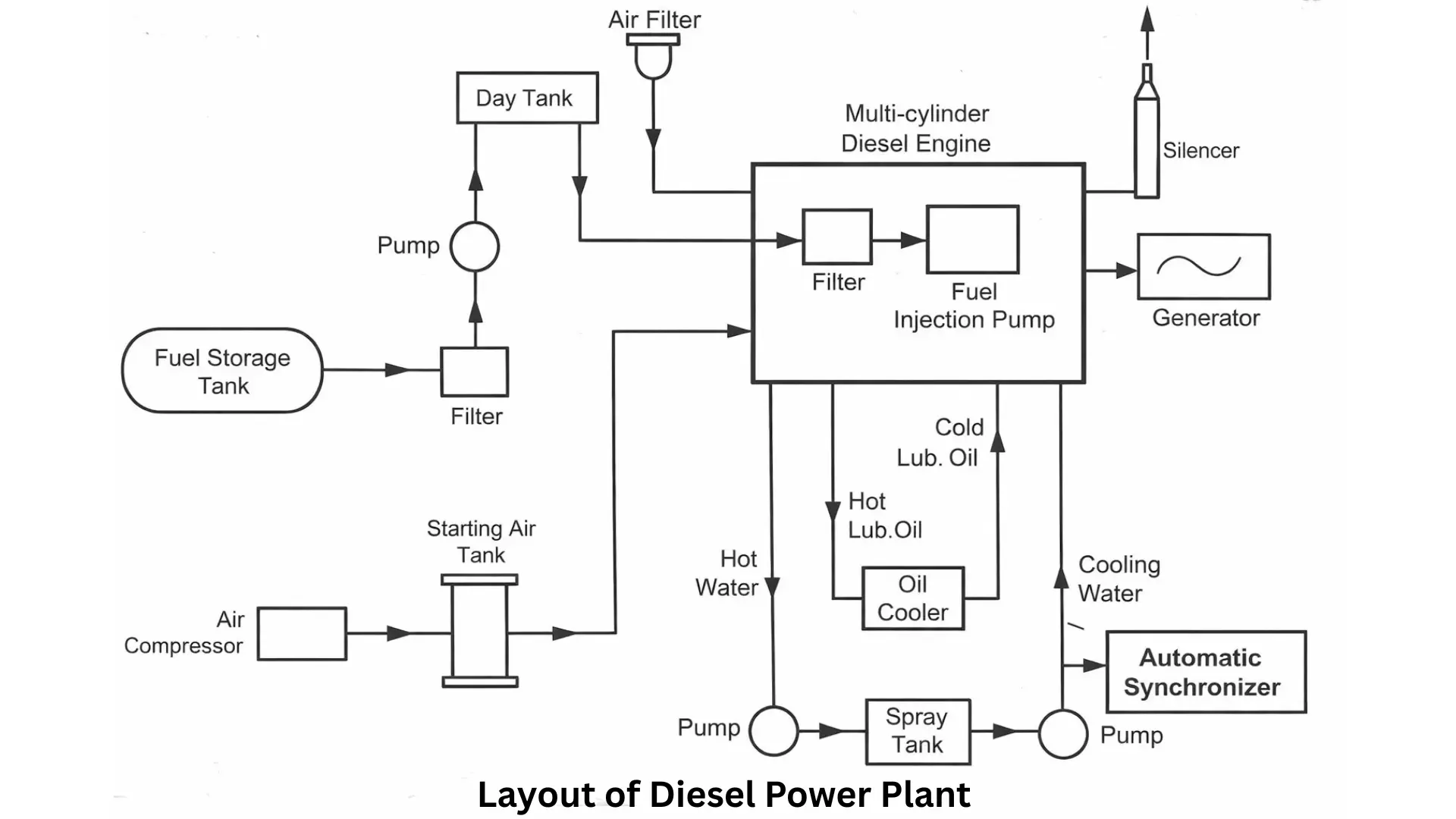
Diesel Engine: Converts the chemical energy of diesel fuel into mechanical energy to drive the generator. Engines can be two-stroke or four-stroke, depending on design. Multi-cylinder engines are often used for higher power output and efficiency.
Air Filter and Supercharger: The air filter removes dust and impurities from incoming air before combustion. The supercharger increases air pressure to improve engine efficiency and performance. Together, they ensure optimal combustion conditions.
Exhaust System: Safely channels exhaust gases out of the engine to the atmosphere. Silencers reduce the noise generated during combustion. The system ensures environmental safety and prevents back pressure in the engine.
Fuel System: Comprises storage tanks, pumps, filters, and fuel injectors. It supplies the engine with the correct amount of diesel based on load demand. The system ensures clean and efficient fuel delivery for consistent operation.
Cooling System: Maintains optimal engine temperature by circulating water or air around hot components. It removes excess heat generated during combustion. Proper cooling prevents engine overheating and damage.
Lubricating System: Supplies oil to moving parts to reduce friction and wear. Lubrication prolongs engine life and ensures smooth operation. The system includes oil pumps, coolers, and tanks for continuous circulation.
Starting System: Provides the initial energy to start the engine using compressed air, electric motors, or batteries. It allows the engine to overcome initial resistance and begin operation. Efficient starting ensures rapid power availability when needed.
Governing System: Controls fuel supply to maintain a consistent engine speed despite variations in load. It prevents engine stalling or overspeeding. The system ensures reliable and stable electricity generation.
Working of Diesel Power Plant
Diesel power plants operate by converting thermal energy into mechanical energy, which is then transformed into electrical energy.
- Air is drawn into the engine cylinder through the air filter, ensuring that only clean air enters for combustion.
- The piston compresses the air, raising its temperature and pressure, which prepares it for fuel ignition.
- Diesel fuel is injected into the cylinder and ignites spontaneously, with expanding gases pushing the piston to generate mechanical energy.
- Spent gases are expelled from the cylinder through the exhaust system, clearing the chamber for the next cycle.
- The engine’s crankshaft drives the alternator, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy efficiently.
- Cooling, lubrication, and governing systems maintain smooth operation and prevent damage from heat, friction, or load variations.
Applications of Diesel Power Plant
Diesel power plants are widely used in many areas:
- Emergency power supply in hospitals, airports, and offices.
- Remote locations where grid electricity is not available.
- Industries and factories for continuous operations.
- Construction sites and mining projects.
- Ships and naval applications as onboard power sources.
Their versatility makes them an essential part of modern power systems.
Advantages of Diesel Power Plant
- Diesel power plants have several benefits:
- Quick start-up and immediate electricity supply.
- Can operate in remote areas without grid access.
- Requires less space compared to other power plants.
- Low installation cost and simpler setup.
- Highly reliable and easy to maintain.
These advantages make diesel power plants very popular worldwide.
Disadvantages of Diesel Power Plant
Despite the benefits, diesel power plants also have some drawbacks:
- High fuel cost compared to other power sources.
- Produces harmful emissions like CO₂ and NOx.
- Noise and vibration during operation.
- Limited efficiency for large-scale power generation.
- Dependence on continuous fuel supply.
It is important to weigh these disadvantages before choosing a diesel power plant.
Conclusion
Diesel power plants provide a reliable and flexible source of electricity for small-scale generation and emergency backup. Their simple design, quick startup, and efficiency make them an ideal choice for areas with limited resources.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks


