Vernier Caliper: Construction, Working, Uses, and Formula
Published: 3 Oct 2025
Measuring tiny dimensions with precision is a critical part of science, engineering, and machining. While a simple ruler can measure rough lengths, instruments like the vernier caliper offer far greater accuracy. This versatile measuring tool is widely used in laboratories, workshops, and industries to measure internal, external, and depth dimensions with ease.
What is Vernier Caliper?
Vernier Caliper Diagram
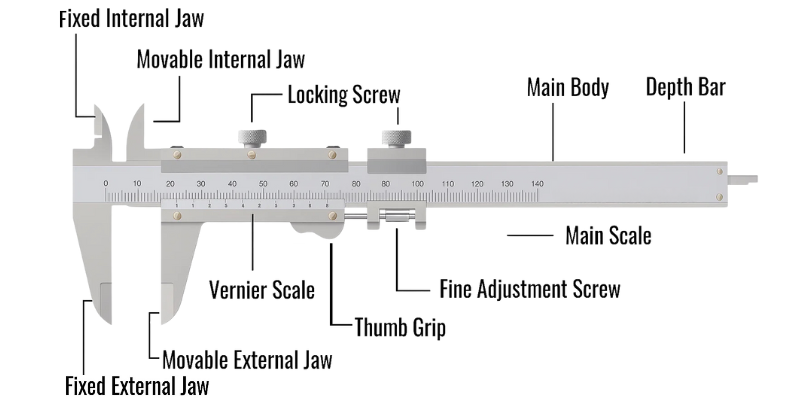
A vernier caliper is a precision measuring instrument designed to measure the thickness, diameter, or depth of objects up to 0.1 mm or even finer. It consists of a main scale and a sliding vernier scale, which allows users to take measurements more accurately than standard rulers. Its design makes it suitable for measuring both internal and external dimensions as well as depth.
Construction of Vernier Caliper
The vernier caliper is constructed from hardened steel, ensuring durability and accuracy. The main scale is a rectangular steel bar graduated in millimeters or centimeters, while the sliding vernier scale is divided into smaller increments for precise readings. Two sets of jaws are attached—one for measuring external dimensions and another for internal dimensions. Additionally, a depth probe is included to measure the depth of holes or recesses.
Vernier Caliper Parts
The key parts of a vernier caliper include:
Outside jaws: Measure the external diameter or width of objects.
Inside jaws: Measure the internal diameter of hollow objects.
Depth probe: A slender rod used for measuring the depth of holes or slots.
Main scale: Provides measurements in millimeters or centimeters.
Vernier scale: Provides readings up to one decimal place in millimeters.
Retainer/Screw lock: Helps to hold the sliding scale in position for transferring measurements.
Working of Vernier Caliper
The working principle of a vernier caliper is simple yet effective. The object is placed between the jaws (or against the depth probe). First, the main scale reading is noted where the zero of the vernier scale aligns. Then, the vernier scale reading is identified by finding which vernier division aligns exactly with any division on the main scale. The final measurement is obtained by adding the main scale reading to the vernier scale reading.
How to Use a Vernier Caliper
Using a Vernier caliper involves the following steps:
- Place the object between the appropriate jaws or against the depth probe.
- Close the jaws gently to avoid errors.
- Note that the main scale reading is just before zero of the vernier scale.
- Find the vernier division that perfectly aligns with the main scale.
- Add the two readings for the final measurement.
- Apply zero error correction if required.
Uses of Vernier Caliper
The Vernier caliper has multiple uses across industries and fields:
- Measuring the thickness of objects such as rods, plates, or sheets.
- Determine the internal diameter of pipes, cylinders, or rings.
- Measuring the external diameter of spherical or cylindrical objects.
- Measuring the depths of grooves, holes, or recesses.
- Commonly used in mechanical workshops, laboratories, and quality control processes.
Vernier Caliper Formula
The formula for measurement using a vernier caliper is:
Measurement = Main Scale Reading (MSR) + Vernier Scale Reading (VSR) × Least Count
This ensures that both the larger divisions of the main scale and the fine precision of the vernier scale are included.
Vernier Caliper Least Count Formula
The least count of a vernier caliper is the smallest value that can be measured accurately. It is calculated as follows:
Least Count = Value of one main scale division ÷ Number of divisions on the vernier scale
For example:
If 1 mm is the smallest main scale division and there are 10 divisions on the vernier scale, then:
Least Count = 1 mm ÷ 10 = 0.1 mm = 0.01 cm
Conclusion
The vernier caliper remains one of the most reliable instruments for precise measurements. From scientific research to industrial manufacturing, its ability to measure internal, external, and depth dimensions makes it indispensable. With its simple construction, accurate working principle, and ease of use, it is no wonder that vernier calipers are still widely used even with the advancement of digital tools.
FAQs
A vernier caliper is used to measure internal diameters, external diameters, thickness, and depths of objects with high accuracy.
The least count of a standard vernier caliper is 0.1 mm or 0.01 cm.
The price of a vernier caliper varies depending on the type and quality. Basic manual models can cost around $10–$30, while digital versions may range from $50 to over $200.
The least count in centimeters is typically 0.01 cm.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks


