Difference Between 2 Stroke and 4 Stroke Engines
Published: 30 Jun 2025
In this article, we’ll explain the difference between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines—clearly and completely—so anyone can understand. Knowing how they work will help you choose the right one for performance, fuel efficiency, and maintenance.
2 Stroke Vs 4 Stroke Engines: The key Differences
2 Stroke
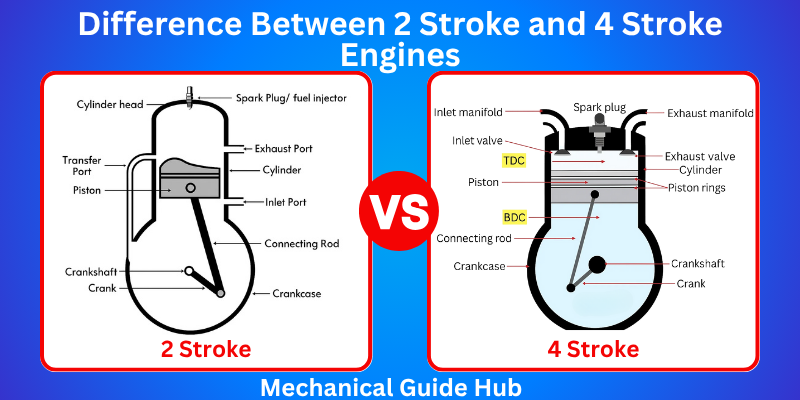
- It Completes a full power cycle in just two stroke moves. The engine fires once every revolution
- It generates higher torque at higher RPM.
- Less efficient because some unburned fuel escapes through the exhaust.
- Produces more smoke due to oil burning with fuel. Higher emissions make it less eco-friendly.
- Oil is mixed with fuel or added through a separate line. It burns during combustion, which also causes carbon build-up.
- Higher wear due to limited lubrication and more heat.
- It has a simple design and uses ports instead of valves, resulting in fewer moving parts.
- In a 2-stroke, no cams or gears are used. The piston controls intake and exhaust timing.
- Lower thermal efficiency because some fuel doesn’t burn completely and gets wasted.
- Delivers power every revolution, giving more power for its size and a higher power-to-weight ratio.
- Needs frequent maintenance. More wear, more cleaning, more spark plug issues.
- Usually air-cooled and can overheat with long use.
- Good for light tools like chainsaws, dirt bikes, and small motors.
4 Stroke
- Needs four piston moves to complete one power cycle (intake, compress, power, exhaust). It fires every two piston moves.
- It offers more consistent torque at lower RPMs.
- It is more fuel-efficient because all the fuel is used in a sealed cycle with no leakage.
- Burns cleaner. Since oil and fuel are separate, it produces fewer harmful gases.
- Uses a separate oil system to lubricate engine parts. This keeps parts cooler and cleaner.
- It wears out less because it uses separate oil and stays cooler.
- It has a more complex design with parts like valves and a camshaft that help run the engine.
- In a 4-stroke engine, cams, gears, and pushrods are used to control the timing of valve operation.
- It gives higher thermal efficiency due to Better cooling and full fuel use
- Produces power every other revolution, leading to smoother running.
- Less frequent service is required. Just regular oil changes and part checks.
- Often has air or liquid cooling. Keeps the engine at a safe temperature during long use.
- Used in motorcycles, cars, scooters, lawnmowers, and other long-running machines.
Conclusion
Both two-stroke and four-stroke engines have their strengths. If you need speed and power for short bursts, a 2-stroke engine might be your go-to. But if you’re after fuel efficiency, less noise, and long-term use, a 4-stroke engine is a smarter choice. Now that you understand the difference between 2-stroke vs 4-stroke engines, it’s easier to choose the one that suits your needs. So, which one will you pick?
Please Write Your Comments


`
Comments (0)

INSTRUCTIONS:
- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

INSTRUCTIONS:
- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks